Forest ThreatNet
Here Today or Here to Stay? ForWarn Monitors Seasonal Duration of Forest Disturbance Impacts
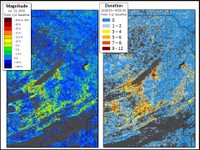 Some disturbances come and go, leaving forests no worse for the wear. Other times, disturbance damage causes longer lasting effects on forests when dieback or mortality results. When viewed from above with coarse resolution remote sensing, such as with satellite imagery or aerial surveys, canopy impacts can appear similar whether disturbance damage is fleeting or more enduring. How can managers gauge the true impacts of forest disturbance on forest growth and productivity? Eastern Threat Center researchers behind the satellite-based ForWarn tool have developed new Seasonal Duration map products that distinguish short-lived disturbances from lasting disturbances. “ForWarn‘s Seasonal Duration products record the count of weekly monitoring periods that fell below a three percent drop in vegetation greenness compared to the prior year,” explains Bill Hargrove, Eastern Threat Center research ecologist and lead ForWarn researcher. “These maps provide a simple way to identify areas that have experienced long lasting change that are easily overlooked due to the low magnitude of the disturbance or persistent cloud cover during the growing season.” Read more in CompassLive...
Some disturbances come and go, leaving forests no worse for the wear. Other times, disturbance damage causes longer lasting effects on forests when dieback or mortality results. When viewed from above with coarse resolution remote sensing, such as with satellite imagery or aerial surveys, canopy impacts can appear similar whether disturbance damage is fleeting or more enduring. How can managers gauge the true impacts of forest disturbance on forest growth and productivity? Eastern Threat Center researchers behind the satellite-based ForWarn tool have developed new Seasonal Duration map products that distinguish short-lived disturbances from lasting disturbances. “ForWarn‘s Seasonal Duration products record the count of weekly monitoring periods that fell below a three percent drop in vegetation greenness compared to the prior year,” explains Bill Hargrove, Eastern Threat Center research ecologist and lead ForWarn researcher. “These maps provide a simple way to identify areas that have experienced long lasting change that are easily overlooked due to the low magnitude of the disturbance or persistent cloud cover during the growing season.” Read more in CompassLive...
« Previous page Next page » Return to contents